Unlocking the Power of Durable Functions; A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, serverless technologies have gained immense popularity for their scalability, cost-efficiency, and ease of use. Microsoft’s Azure Functions is a shining example of serverless computing, and within this ecosystem lies a powerful extension called Durable Functions. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into what Durable Functions are, their key features, and why you should consider using them in your applications.
What is Durable Functions?
At its core, Durable Functions is an extension of Azure Functions that enables developers to create stateful functions in a serverless compute environment. This extension introduces a new level of abstraction, allowing you to define stateful workflows through orchestrator functions and stateful entities via entity functions, all within the familiar Azure Functions programming model. Behind the scenes, Durable Functions takes care of managing state, handling checkpoints, and facilitating restarts, providing a robust foundation for building complex and reliable workflows.
Supported Patterns
Durable Functions supports a wide range of patterns, making it a versatile tool for various scenarios:
- Function Chaining: Link multiple functions together to create a chain of execution.
- Fan-out/Fan-in: Execute multiple tasks concurrently and aggregate the results.
- Async HTTP APIs: Build asynchronous HTTP APIs easily.
- Monitoring: Gain insights into the execution and progress of your workflows.
- Human Interaction: Incorporate human interaction steps into your workflows.
- Aggregator (Stateful Entities): Maintain stateful entities to track and aggregate data.
For more in-depth information on Durable Functions and these patterns, you can refer to the official documentation.
Why Choose Durable Functions?
Now that we have a basic understanding of what Durable Functions are, let’s explore the compelling reasons why you should consider integrating them into your serverless applications:
1. Express Workflows in Code
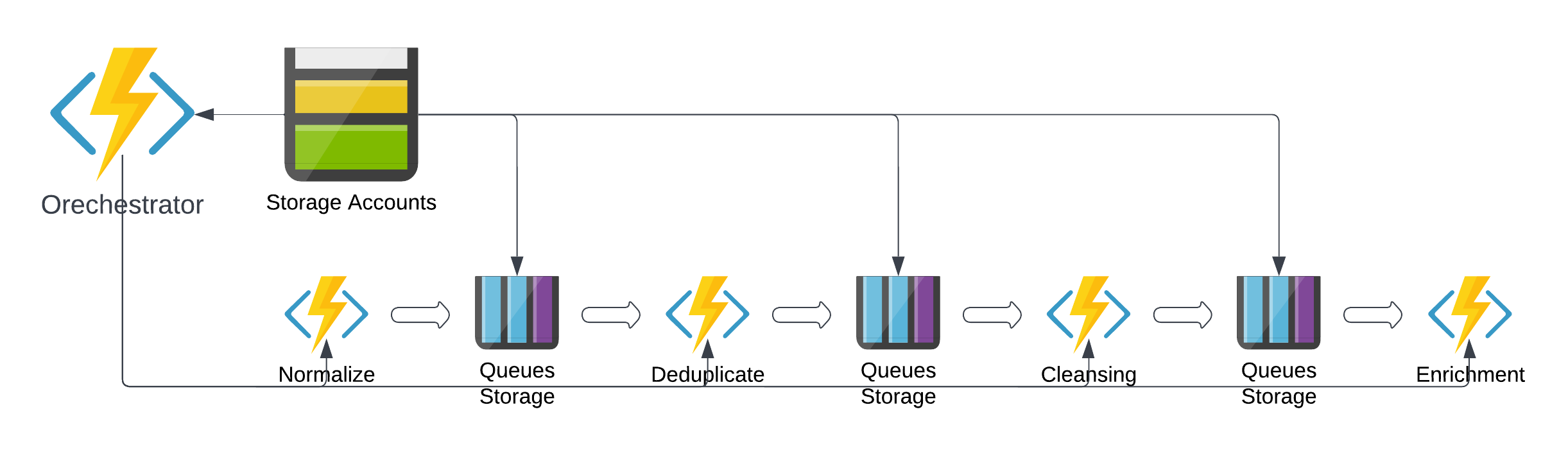
Durable Functions empower you to define complex workflows directly in code. This capability simplifies the orchestration of functions and enables you to create structured, readable code for your business processes. For instance, here’s an example of a function chaining implementation:
Example for chaining.
Code implementation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// Example of function chaining
[FunctionName("Orchestrator_Chaining")]
public static async Task<object> Run(
[OrchestrationTrigger] IDurableOrchestrationContext context)
{
try
{
var normalizedEntity = await context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Normalize", entity);
var deduplicatedEntity = await context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Deduplicate", normalizedEntity);
var cleansedEntity = await context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Cleansing", deduplicatedEntity);
return await context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Enrichment", cleansedEntity);
}
catch (Exception)
{
// Error handling or compensation logic goes here.
}
}
2. Retry Activities
Durable Functions offer built-in support for retrying activities with back-off strategies. You can easily add retries to individual activity functions and sub-orchestrations, enhancing the resilience of your workflows against transient errors.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
[FunctionName("TimerOrchestratorWithRetry")]
public static async Task Run([OrchestrationTrigger] IDurableOrchestrationContext context)
{
var retryOptions = new RetryOptions(
firstRetryInterval: TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5),
maxNumberOfAttempts: 3);
await context.CallActivityWithRetryAsync("Normalize", retryOptions, entity);
// ...
}
3. Run Activities in Parallel
Parallelism is a breeze with Durable Functions, and implementing “fan-in” patterns is straightforward. Running activities in parallel can significantly boost the efficiency of your workflows.
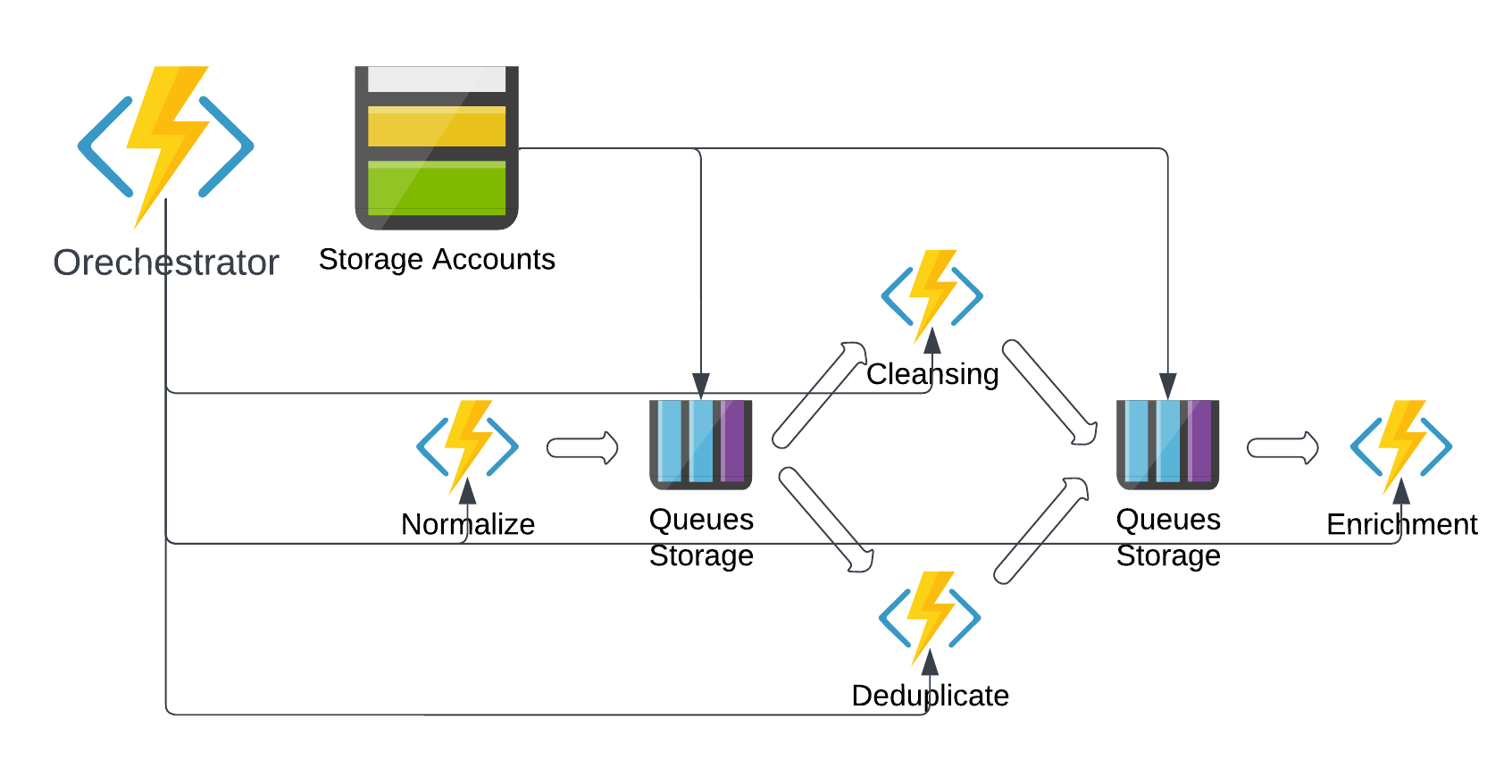
Example for parallel.
Code implementation.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
[FunctionName("FanOutFanIn")]
public static async Task Run(
[OrchestrationTrigger] IDurableOrchestrationContext context)
{
var parallelTasks = new List<Task<object>>();
var normalizedEntity = await context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Normalize", entity);
// Define a list of work items to process in parallel.
parallelTasks.Add(context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Cleaning", normalizedEntity));
parallelTasks.Add(context.CallActivityAsync<object>("Duplicate", normalizedEntity));
await Task.WhenAll(parallelTasks);
// Aggregate the results and send them to Enrich.
object[] cleansedDeduplicated = parallelTasks.Select(t => t.Result).ToArray();
await context.CallActivityAsync("Enrichment", cleansedDeduplicated);
}
4. State Management for Free
Durable Functions take care of managing workflow states, eliminating the need for you to maintain your own database. It transparently handles state-related queues and table storage on the associated storage account. Keep in mind that Durable Functions assume that all activities are idempotent, caching requests and responses to improve performance, even during replays.
5. Check Workflow Progress with REST API
Durable Functions provide a powerful REST API for monitoring the progress of your orchestrations. You can query the status of running orchestrations, view their execution history, and even store custom status information for diagnostic purposes.
Here are a few essential API endpoints:
- Starting a function:
POST /runtime/webhooks/durabletask/orchestrators/{functionName}/{instanceId} - Getting status:
GET /runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/{instanceId} - Purging instances:
DELETE /runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/{instanceId}
For detailed explanations and parameters, refer to the official documentation.
6. Versioning Made Easier
Dealing with versioning in workflow implementations can be challenging. Durable Functions offers strategies for handling version updates without disrupting in-flight orchestrations. Some strategies include upgrading when no workflows are in progress and supporting side-by-side deployments with older versions. For more details, check the documentation.
7. Default Integration with Azure Application Insights
Durable Functions seamlessly integrate with Azure Application Insights, providing robust observability and monitoring capabilities for your workflows.
8. Serverless Pricing Model
Azure Functions, including Durable Functions, follow a serverless pricing model. You only pay for the resources you consume during execution, making it cost-effective and scalable.
9. Azure Function Kubernetes Support
If you’re using Kubernetes in your infrastructure, Azure Functions, including Durable Functions, now have support, allowing you to leverage Kubernetes for deploying and scaling your serverless applications.
10. Develop and Test Locally
Durable Functions can be developed and tested locally, providing a smooth development experience. You can build and debug your workflows on your development machine before deploying them to the cloud.
Conclusion
Durable Functions are a powerful extension of Azure Functions that simplify the development of complex, stateful workflows in a serverless environment. Whether you need to express intricate business processes, handle retries, run tasks in parallel, or manage state effortlessly, Durable Functions have you covered. With built-in support for monitoring, versioning, and serverless pricing, they are a valuable addition to your serverless toolkit. So, if you